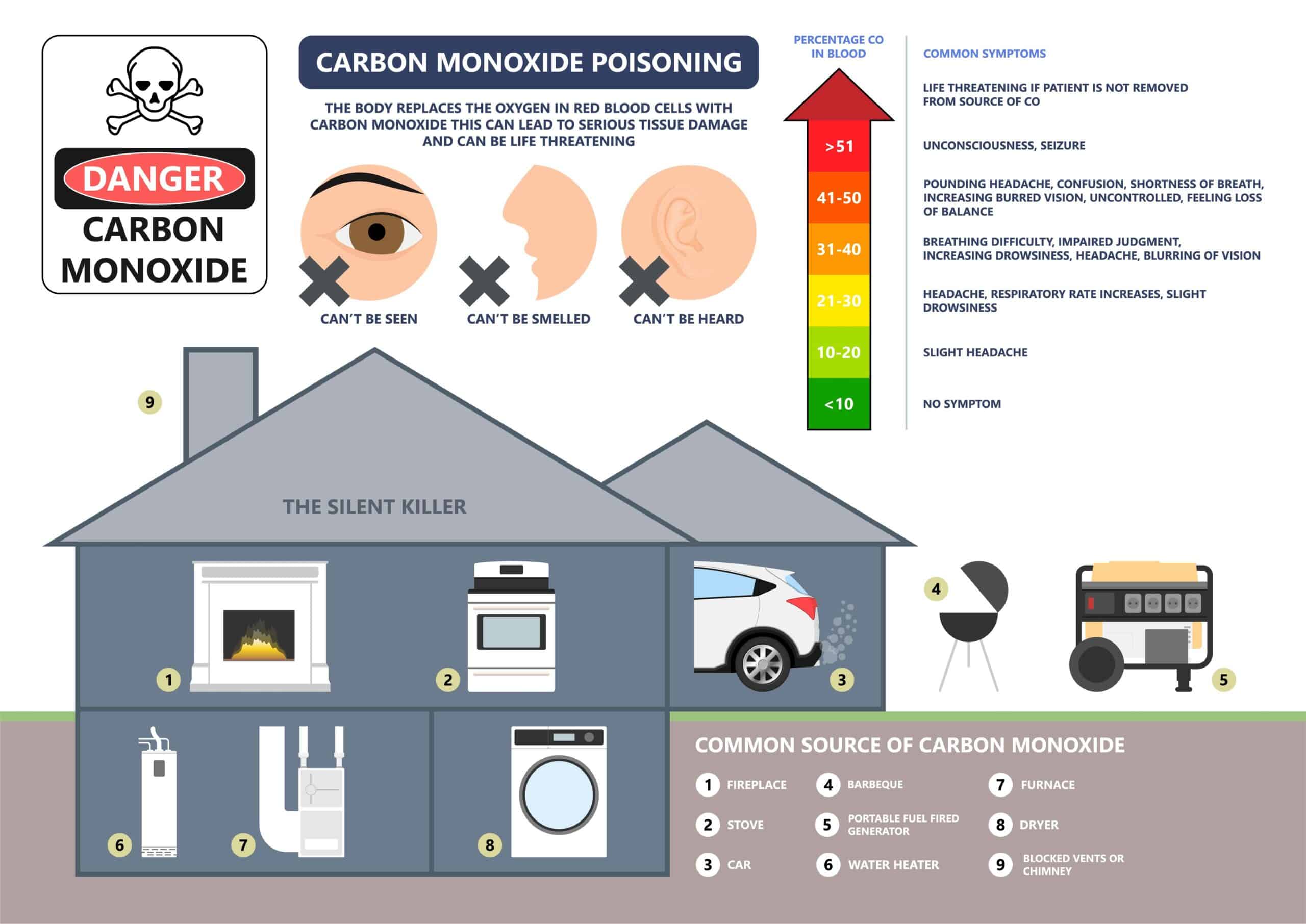
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a gas that is colorless and odorless. This common industrial hazard is created when fuels containing carbon do not completely combust. Breathing in too much CO can cause severe illness or even death in humans. Carbon monoxide poisoning can happen at home or the workplace.
Learn what happens when carbon monoxide is inhaled, how to detect carbon monoxide, how to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning, and what to do if you suspect the presence of carbon monoxide in your commercial facility.
How Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Happens
Carbon monoxide poisoning occurs when there is too much CO in the air, often as the result of inhaling combustion fumes. The human body replaces the oxygen in red blood cells that’s required for your body to function with CO. When this occurs, oxygen is unable to reach your body’s organs and tissues, resulting in carbon monoxide poisoning.
Because carbon monoxide is colorless and odorless, it’s hard for humans to detect its presence without the use of technology. This means that CO can go undetected and that workers can breathe it in for quite some time before feeling the effects of carbon monoxide poisoning. Symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning include: blurred vision, confusion, dizziness, headache, loss of consciousness, nausea/vomiting, shortness of breath, and weakness.
How Carbon Monoxide is detected
Known as a “silent killer,” carbon monoxide is almost undetectable unless a detection device is used. These devices make use of a silicon microchip that sends an electrical charge to a sensor. This sensor is housed in a small detection chamber and measures CO concentration in the atmosphere. When CO levels reach a certain threshold, an alarm will sound.
How to Prevent Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
According to The American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 13% of nonfatal carbon monoxide poisoning cases seen in U.S. emergency departments were exposed at work. The best ways to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning in the workplace include installing decent CO detectors and ensuring that your facility has proper ventilation for the machinery/operations being housed. It’s also important to keep up with regular maintenance to ensure your machinery is functioning properly.
When possible, it may be beneficial to switch from gasoline powered equipment to electric or battery powered equipment, as the less combustion that takes place in your facility, the lower the chance of a concentration of carbon monoxide building up. If there is a known potential risk for carbon monoxide poisoning, employees should be outfitted with personal CO monitors that have audible alarms. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) prohibits worker exposure to more than 50 parts of CO per million parts of air averaged during an eight hour time period.
What To Do If You Suspect Carbon Monoxide
If you suspect the presence of carbon monoxide in your workplace or a CO detection alarm sounds, immediately move outside for fresh air. If possible, open any windows, doors, and vents to allow as much ventilation as possible. If anyone is experiencing carbon monoxide poisoning side effects, it’s important for them to promptly seek medical care.
It’s important to isolate the source of carbon monoxide so that you can remove or replace it, and avoid the buildup from happening again.
Consider Fire Systems, Inc.
Should you need any help isolating the source of carbon monoxide or installing CO detectors, consider Fire Systems, Inc. Our highly trained technicians will arrive prepared to tackle any of your commercial facility’s fire and/or carbon monoxide needs.
Founded in 1986, Fire Systems, Inc. is the Atlanta-area’s go to for all aspects of industrial fire protection. If you have any questions or concerns about your building’s fire safety, give us a call at 770-333-7979 or visit our website today.